
- #How to calculate ppm in air carbon dioxide measured how to
- #How to calculate ppm in air carbon dioxide measured iso
- #How to calculate ppm in air carbon dioxide measured free
Ventilation Efficiency - The efficiency of a ventilation system may be related to temperature and/or pollution concentrations.
#How to calculate ppm in air carbon dioxide measured how to
Solutions, Molarity and Dilution - Definitions and examples of how to calculate wt%, molarity and how to prepare dilutions. Soft or Hard Water - Carbonates dissolved in water. Particle Size - The size of dust particles, pollen, bacteria, virus and many more. Oxygen and Corrosion of Steel Pipes - Oxygen concentration and temperature and the influence on corrosion of steel pipes. Diffusion constants for several gases in water. Gases Solved in Water - Diffusion Coefficients - Diffusion flux tells how fast a substanse solved in another substance flows due to concentration gradients. #How to calculate ppm in air carbon dioxide measured iso
Clean Rooms - ISO Standard 14644 - Clean room class limits according ISO Standard 14644-1.
#How to calculate ppm in air carbon dioxide measured free
Clean Rooms - Federal Standard 209 - Clean rooms virtually free of contaminants like dust or bacteria. Apothecaries' Weight System - Apothecaries' fluid and weight system - ounce, drachms, grains, scruples. Ammonia - NH 3 - Concentration in Air and Health Effects - Ammonia and health symptoms - smell and threat to life. Air Contaminants - Limits - Permissible limits to exposure of various air contaminants. Basics - The SI-system, unit converters, physical constants, drawing scales and more. Molality is the number moles of solute divided by kilograms of solvent. Molarity is the number of moles of solute (substance of interest - pollution, etc.) dissolved in one liter (volume) of the solution. Percent by volume = 100 v c /(v c + v s) (3) Volume percent can be expressed as volume per unit volume: The volume of carbon dioxide in one 1 m 3 of air can be calculated by modifying (1) to The concentration of carbon dioxide in air is aprox. = 8.345 pounds per million gallons of water Example - Volume Concentration of Carbon Dioxide in Air Weight of substance added to one unit volume of water to give one part per million (ppm) The concentration of a component can be measured as mass per unit volume - like mg/liter, mg/cm 3 etc. Weight percent = 100 m c / m s (2) ppm vs. ppq - parts per quadrillion (1 / 1,000,000,000,000,000 or 10 -15)Īn alternatively mass related unit to measure larger concentration levels is weight percent which can be expressed as. 
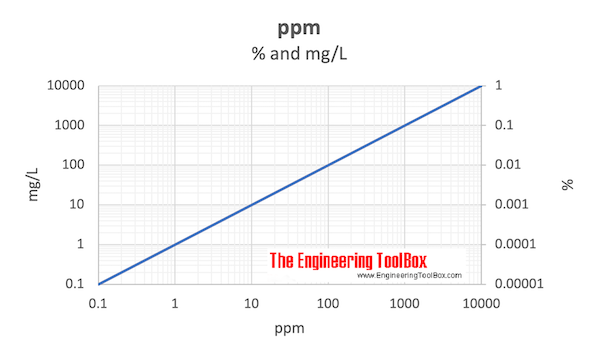
percent and mg/L chartĪlternatively - mass related units to measure very small concentration levels: In the metric system ppm for mass can be expressed in terms of milligram versus kg whereĭownload and print ppm vs. S = molar mass, volume or mass of solution (mole, m 3, ft 3, kg, lb m) ppm is defined asĬ = molar mass, volume or mass of component (mole, m 3, ft 3, kg, lb m) Parts per million is the molar mass, volume or mass ratio between the pollutant component and the solution. Parts per million - ppm - is commonly used as a dimensionless measure of small levels (concentrations) of pollutants in air, water, body fluids, etc.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
